Regulator high pressure definitions
A pressure regulator is a control valve that reduces the input pressure of a fluid to a desired value at its output. When the medium conditions (inlet pressure, medium flow) change, the regulator can still maintain a stable outlet pressure and flow within a certain range.
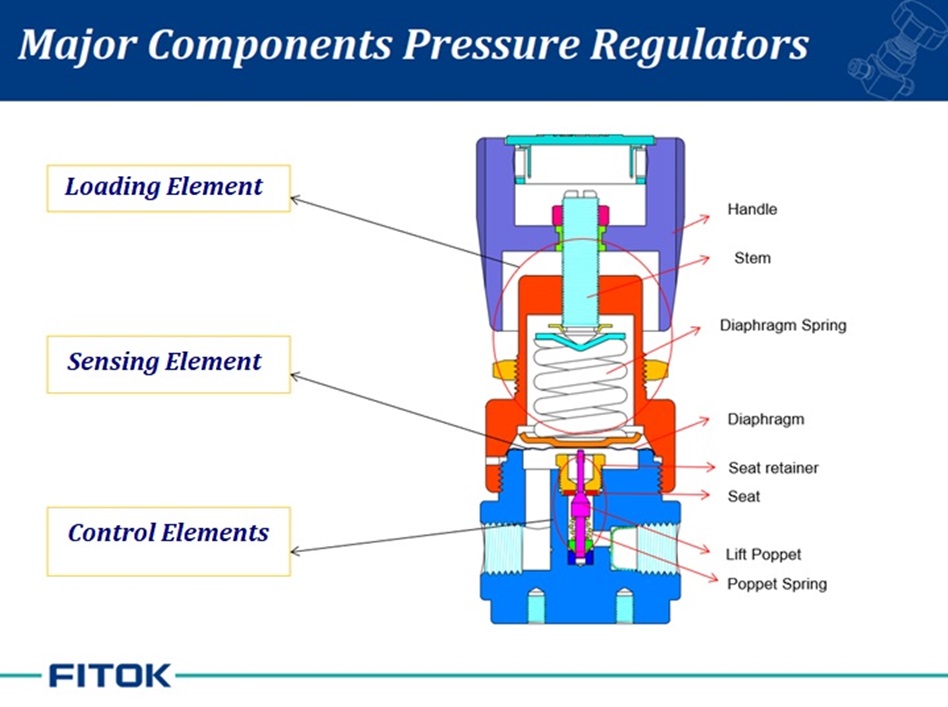
Major Components
- Loading element
- Sensing element
- Control element
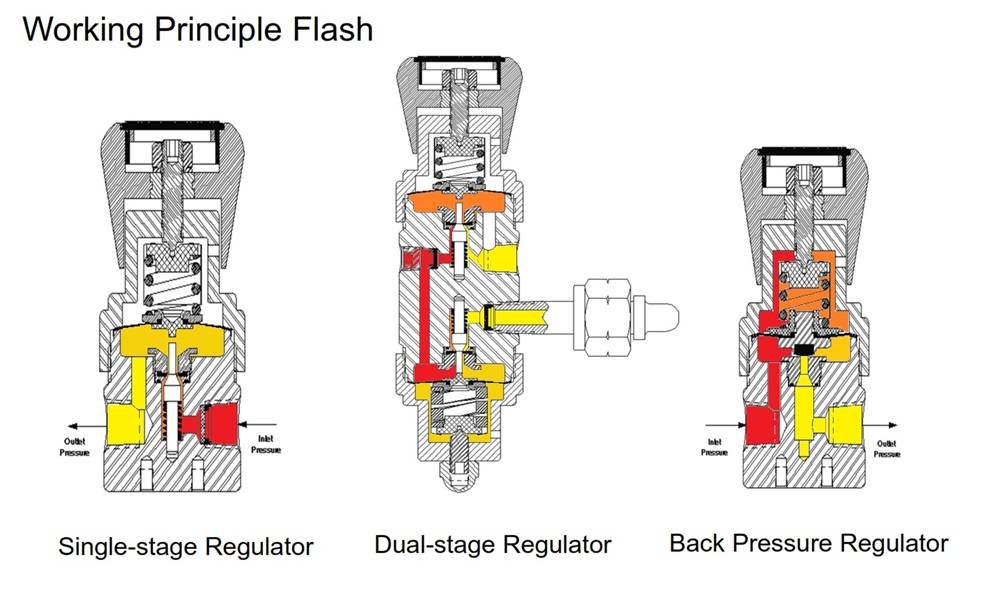
Working Principle
High pressure gas flows through a small orifice into a large space, causing the pressure to reduce. Pressure regulator is about balance of forces.
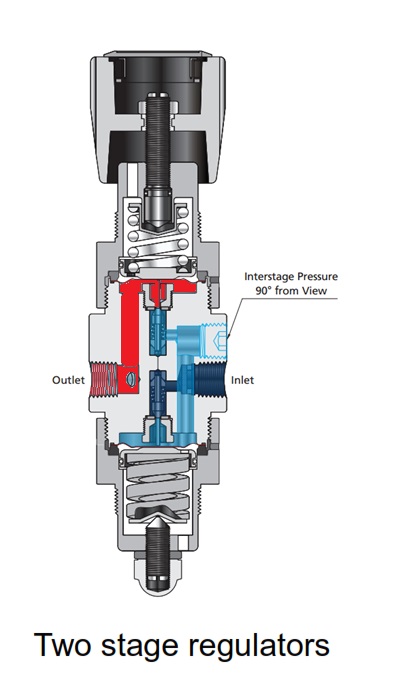
Two stage regulators Working Principle
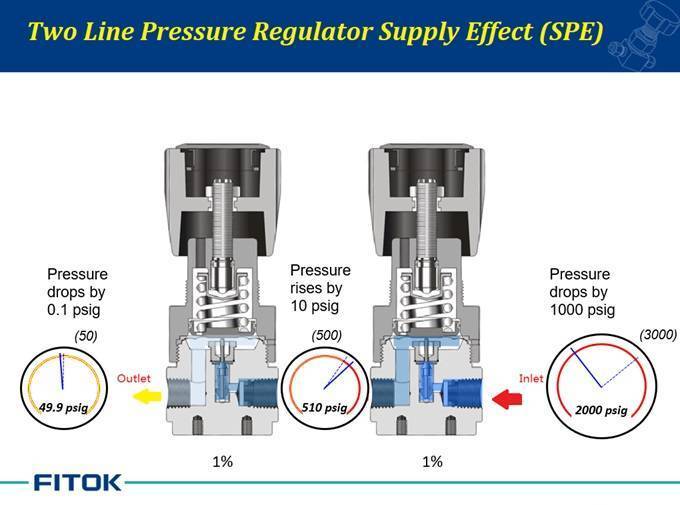
Two stage regulators are two single stage regulators in one that operate to reduce the pressure in two stages instead of one. SPE is reduced to 1%×1%,as the application in FCR-1D.
When the inlet pressure falls to the first stage outlet pressure, the first stage regulator will remain open, and the SPE will recover back to 1%.
Types of loading elements
a. Spring loading (Figure 1)
As the most common types of loading, it is space-saving, convenient and cost effective; However, the increase of outlet flow will cause the pressure drop.
b. Pneumatic loading
Commonly used for high pressure application, and the ratio of pneumatic loading pressure to the outlet pressure is 7:1.
Types of sensing elements
a. Diaphragm sensing
Greater sensitivity with large diaphragm areas and material choices of 316L, Elgiloy, Hastelloy C-22/C-276, Alloy X-750.
Advantages: Greater sensitivity and simplicity, suitable for ultra high purity applications.
Disadvantages: Output pressure 500 psig max. and overpressure will cause the diaphragm rupture.
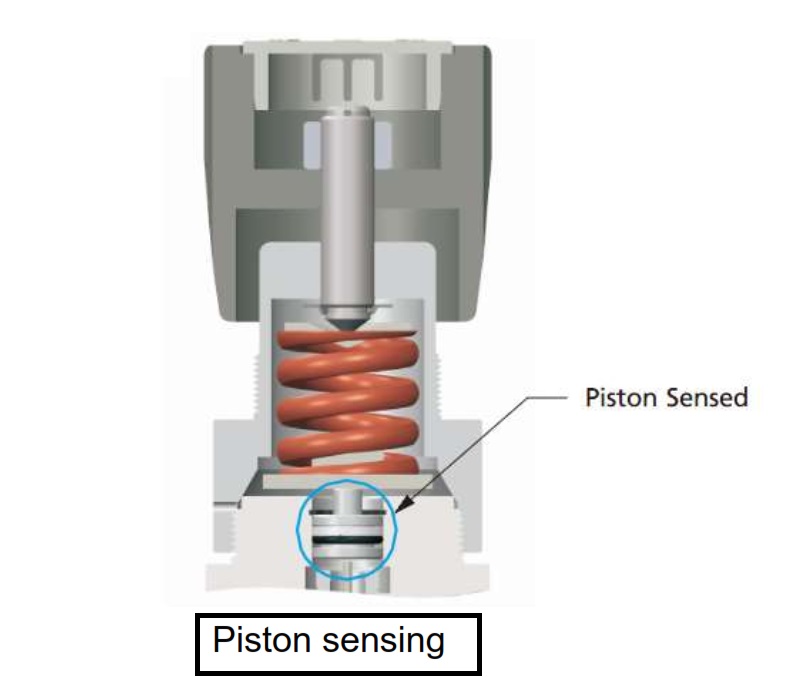
b. Piston sensing
High outlet pressure up to 10,000 psig and dynamic sealing achieved through the combination the piston and O-ring
Advantages: Constant sensing area for reliability Disadvantages: Less sensitivity with O-ring sealing; not intended for ultra high purity application due to lubrication.
Types of control elements
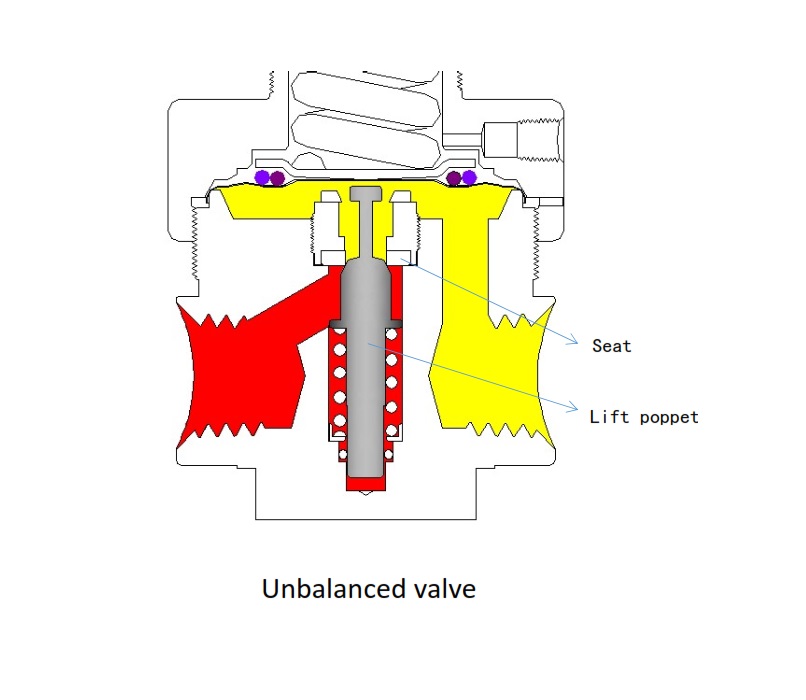
a. Unbalanced poppet
For unbalanced poppet, poppet area is subject to influence of the inlet pressure.
• Advantages:
Inlet pressure provides additional force to enhance the engagement between the poppet and the seat
• Disadvantages:
When the inlet pressure falls, the outlet pressure rises. This often happens when steel cylinders is used as a source of gas. When the inlet pressure is high, the seat is subjected to a large force, requiring a hard seat.
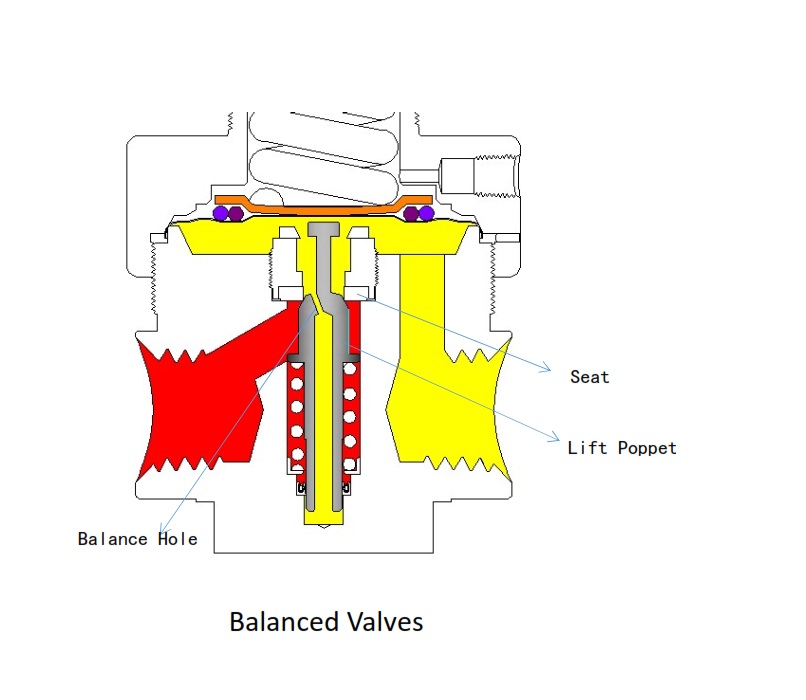
b. Balanced poppet
For balanced poppet, poppet area is almost unaffected by the inlet pressure
Advantages:
The poppet has a balance hole that connects the outlet chamber to the bottom of the valve body, reducing the poppet area which the inlet pressure acts on. When the inlet pressure falls, the outlet pressure rise is not significant.
Disadvantages:
The poppet has large diameter, which allows for large flow. But it is not suitable for small flow control, and needs higher cost.
Types of Regulators
Classified into following types based on applications:
Water pressure regulators: Large cast valve bodies; for process pipelines, see Fig.a. is for Welding gas regulators: mainly brass cast bodies, other materials available, see Fig.b is for Specialty gas pressure regulators: Stainless steel or brass bar stock bodies, see Fig.c. is for Ultra high purity gas regulators: 316L SS bar stock bodies; more clean than specialty gas regulators, see Fig.d.

Specialty gas regulators
• FITOK mainly provides specialty gas regulators and ultra high purity gas regulators.
• Typical structure of FITOK diaphragm-type specialty gas regulators.
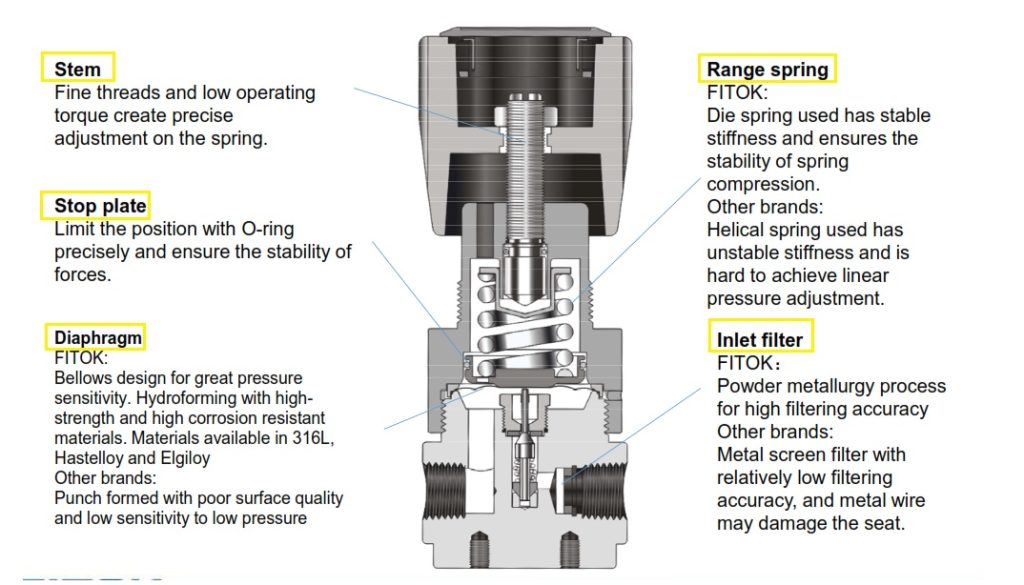
Ultra high purity regulators
Compared to specialty gas regulators, ultra high purity regulators have a higher degree of cleanliness due to the use of tied diaphragm, which means that poppet, diaphragm and the hard core are connected together.

Advantages:
a. Bi-directional poppet sealing (both the inlet pressure and outlet pressure can exert force on the poppet to close against the seat), and enhanced safety.
b. No threads or springs in wetted areas to ensure clean operation
Features :
1.Standard with Hastelloy poppet and diaphragm for high strength and good corrosion resistance.
2. 20 μm filter installed at inlet.
3. No lubricant in the wetted areas
4.Standard inner roughness:
NPT ends: Ra 25 μin. (0.6 μm)
FR ends and TB ends: Ra10 μin. (0.25μm)
5. Electropolished inner surface roughness of Ra 5 μin. (0.13 μm) optional
6. Specialty gas regulators standard with FC-02 Special Cleaning and Packaging Process
7. Multiple choices of processes for ultra high purity pressure gas regulators
Application
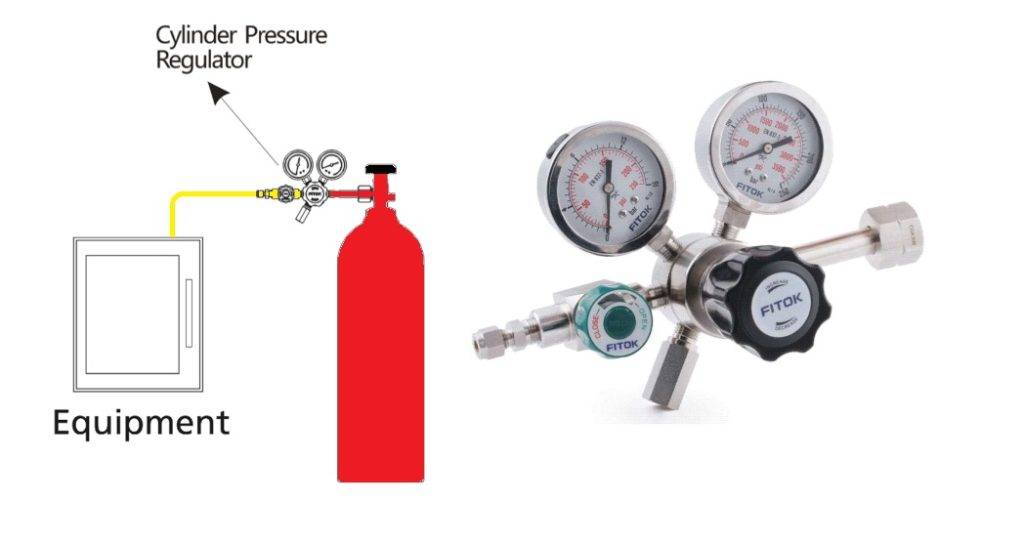
Main Applications
Inlet with cylinder connections to connect to the cylinder

Installed on the lines with a relatively low pressure
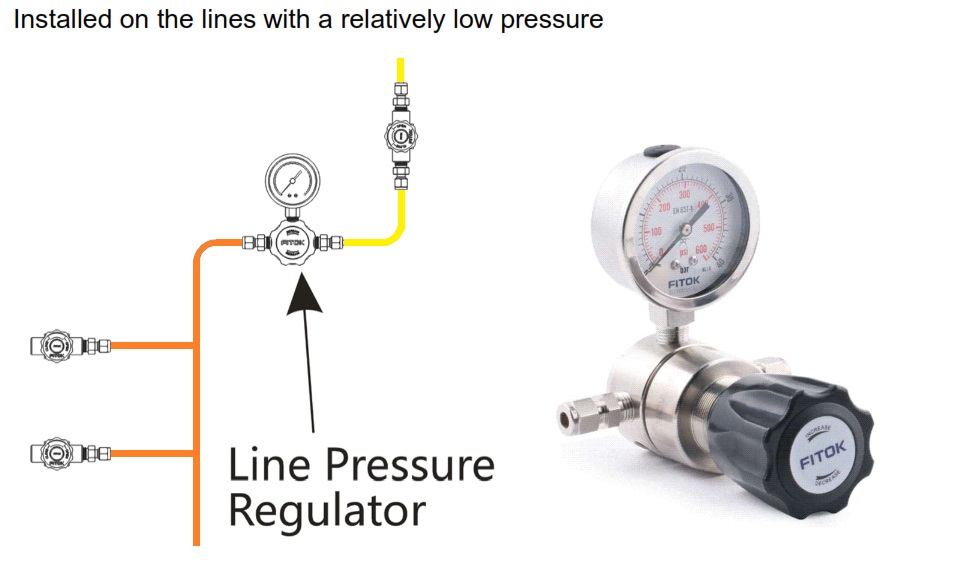
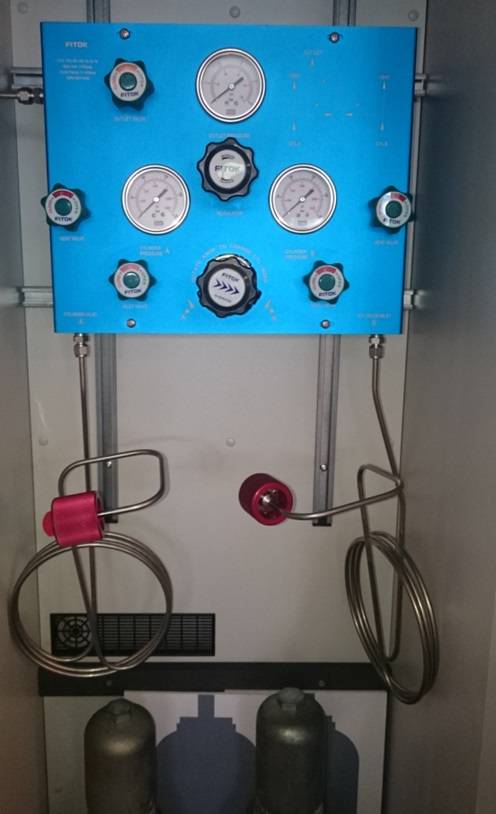
Used with globe valves and pressure control panels
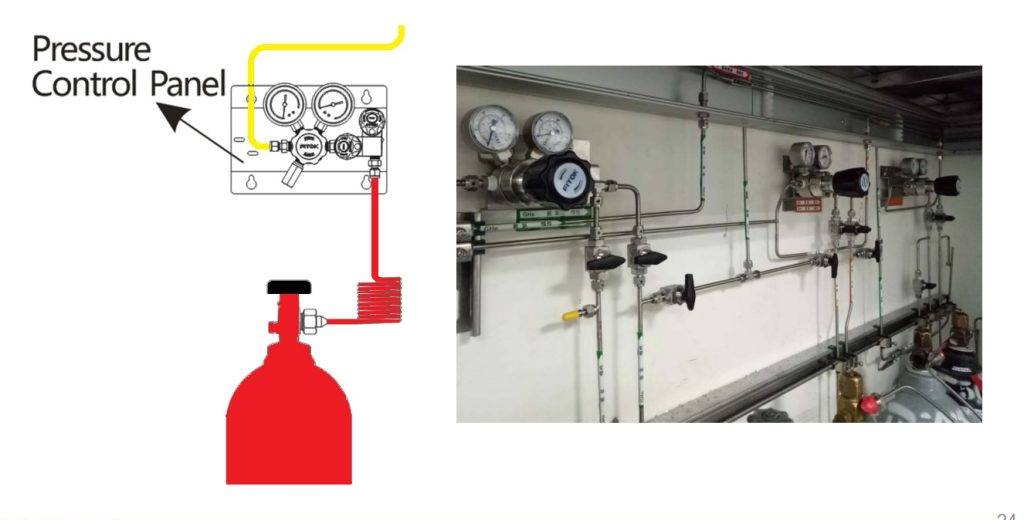
Used with diaphragms valves to form a integrated device such as changeover systems

Malfunction Analysis
Outlet pressure keeps increasing without changing the handle position
Possible reasons : When particles are present in the system, under the effect of high-speed airflow, the particles impact the sealing surface of the valve seat which is generally made of non-metal materials and can be easily damaged. It is recommended to install the filter in the nearest upstream location.
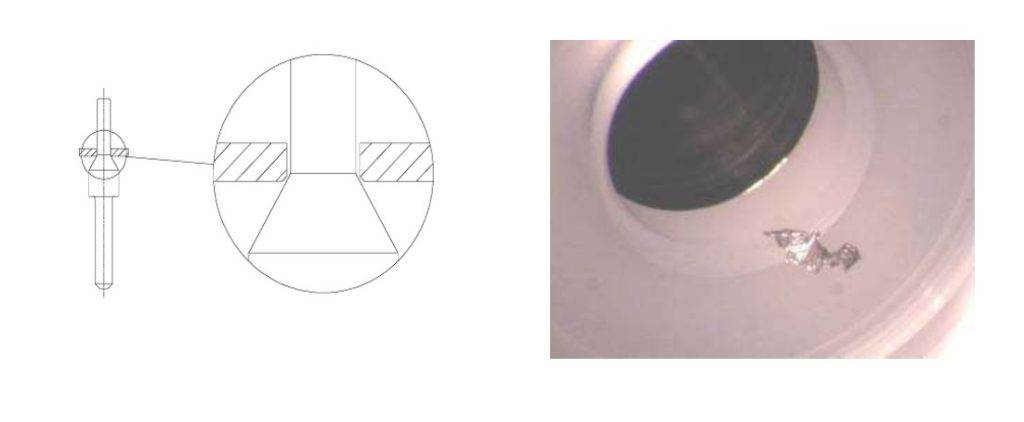
There is no flow when the regulator opens or when there is fluid flowing in the regulator, the output pressure drops suddenly.
Possible reasons: The inlet is clogged. Replace a new filter screen



